Gateway — Local MCP Proxy
The McpMux Gateway runs on localhost:45818 and routes MCP requests from AI clients to the correct servers with automatic authentication and permission filtering.
The Gateway is the core of McpMux — a local HTTP server that acts as a single entry point for all your AI clients. Instead of configuring each client to connect to each MCP server individually, every client connects to the gateway at http://localhost:45818/mcp.
How It Works
Cursor ──────────┐
Claude Desktop ──┤
VS Code ─────────┤──→ McpMux Gateway ──┬──→ GitHub Server
Windsurf ────────┤ (localhost:45818) ├──→ Slack Server
ChatGPT ─────────┘ ├──→ PostgreSQL Server
└──→ Filesystem ServerThe gateway receives MCP JSON-RPC requests from clients and:
- Authenticates the client using its access key
- Resolves which Space the client should use (based on connection mode)
- Collects the client's FeatureSet grants for that Space
- Filters the available tools, resources, and prompts based on permissions
- Routes each request to the correct backend MCP server
- Returns the response to the client
Request Routing
When a client calls a tool (e.g., github_create_issue), the gateway:
- Looks up which server provides that tool
- Checks that the client has permission to use it (via FeatureSets)
- Forwards the request to the server's active connection
- Returns the server's response to the client
Clients only see tools they have permission to use. If a FeatureSet excludes a tool, the client doesn't even know it exists — it won't appear in tools/list responses.
FeatureSet Filtering
The gateway enforces permissions at the protocol level:
tools/list— only returns tools the client is permitted to usetools/call— rejects calls to tools the client doesn't have access toresources/list— only returns permitted resourcesprompts/list— only returns permitted prompts
This means you can have multiple clients connected to the same gateway with different levels of access, all managed through FeatureSets.
OAuth Token Management
For servers that use OAuth 2.1 + PKCE authentication, the gateway handles the full token lifecycle:
- Initial authorization — opens a browser for you to log in and grant permissions
- Token storage — tokens are encrypted and stored in the OS keychain
- Automatic refresh — when a token expires, the gateway refreshes it transparently
- Re-authorization — if a refresh fails, McpMux prompts you to re-authenticate
You never need to manually manage OAuth tokens — the gateway takes care of it.
Connection Pooling
The gateway maintains a pool of connections to backend MCP servers:
- Each server gets a connection based on its configuration and credentials
- Connections are reused across clients (when they share the same Space and credentials)
- The pool key is computed from
server_id + sha256(final_config_with_credentials) - When credentials change (e.g., token refresh), a new connection is created with the updated credentials
- Idle connections are cleaned up after a configurable timeout
This means if two clients in the same Space both use the GitHub server, they share a single connection to GitHub — reducing resource usage.
Starting and Stopping
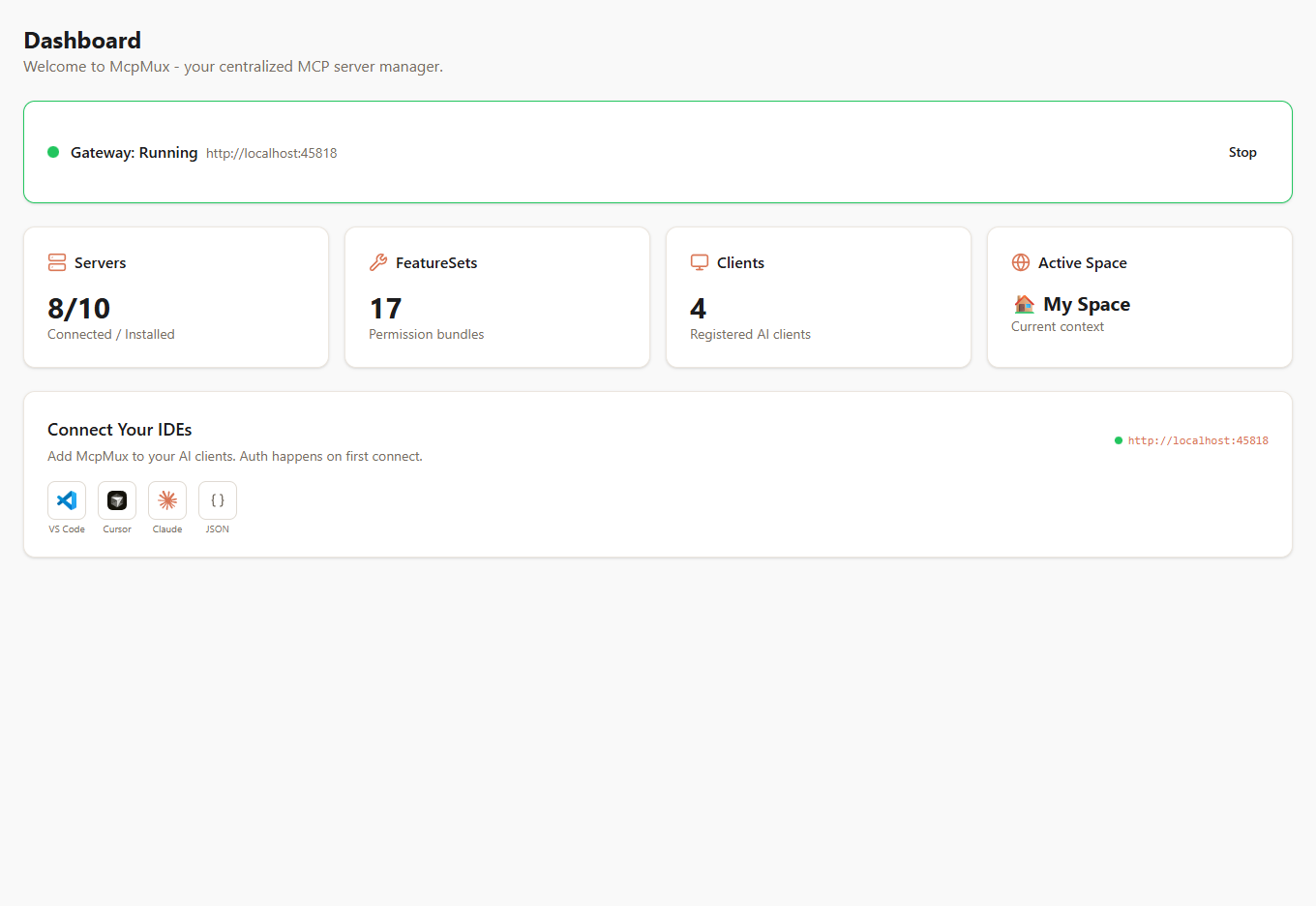
Control the gateway from the Dashboard in McpMux:
- Start Gateway — begins listening on
localhost:45818and connects to enabled servers - Stop Gateway — disconnects all servers and stops accepting requests
The gateway also starts automatically when McpMux launches (configurable in Settings).
Gateway Status
The dashboard shows real-time gateway status:
- Running / Stopped — whether the gateway is accepting connections
- Connected Servers — count of actively connected backend servers
- Registered Clients — count of AI clients that have connected
Next Steps
- Set up Clients to connect your AI applications
- Configure FeatureSets to control what each client can access
- Manage Servers to add and configure backend MCP servers
- Learn about Security to understand how the gateway protects your credentials
Server Management
Install, configure, and manage MCP servers in McpMux. Supports stdio and HTTP transports with encrypted credential storage, environment variable overrides, and OAuth authentication.
Server Definitions — Registry Schema
Learn how to create MCP server definitions for the McpMux registry. Complete JSON schema reference with field descriptions, transport types, input metadata, authentication, and examples.